
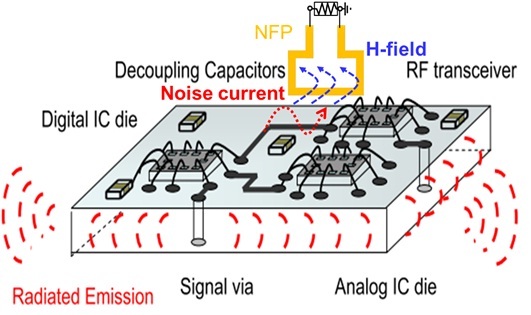
As the complexity of hardware architecture keeps increasing in recent decades, the identifications of noise sources become more challenging. Meanwhile, due to the decreasing of the operating voltage and the noise margin, the performance of radio-frequency (RF) integrated circuits is easily degraded by some weak noise at its frequency range. Therefore, techniques to detect ultra-low noise sources inside the system within specified RF bandwidth is urgent to be developed.
The near-field probes (NFPs) have been widely studied recent years because of their ability to quantify the near-field (electrical or magnetic field) strength in the space close to the noise sources. Most of the studies about the NFPs focused on the improvement of space resolution, available bandwidth, and suppressing the coupled field in orthogonal direction or adverse field.
The design of the multi-direction NFPs is one of our research interests. Different from the conventional one-direction NFP, the multi-direction NFP can accelerate the measurement speed by obtaining the field-strength information of multiple directions with only one measurement step.